Threading Value from Industry and Internal Standards Across Systems
In January, Accuris introduced Accuris Thread, a powerful new tool designed to dramatically reduce the time required to decompose large, complex engineering documents into requirements. Traditionally, this process could take 2–3 hours per page, translating to over a week of manual effort for small to mid-sized documents.
Thread automates this process, identifying and converting requirements into structured digital objects that can be seamlessly exported to leading requirements management and PLM platforms. Customers have reported document processing times as fast as 15 minutes, along with accuracy improvements from 70% accurate to over 90% accurate – Thread even identified critical requirements that had been previously overlooked. Thread also supports design activities and decision-making in engineering workflows by ensuring that requirements are accurately captured and integrated into the design process.
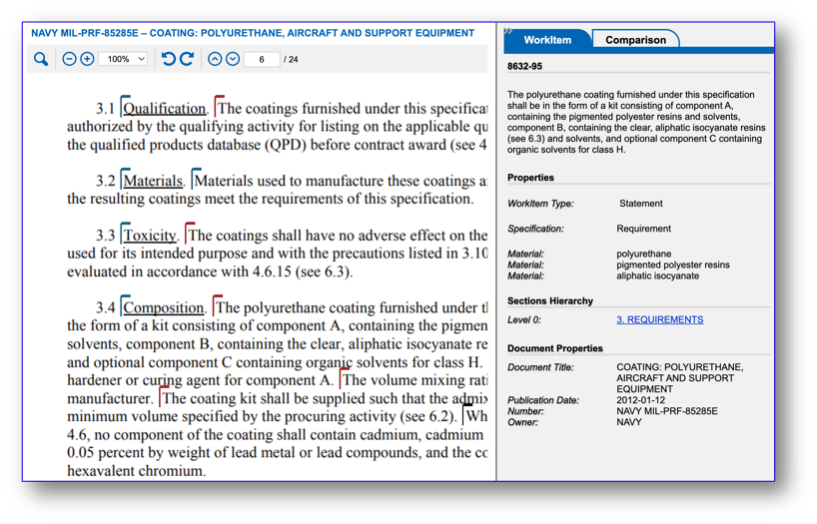
Because Thread is integrated with Engineering Workbench (EWB) – the world’s leading platform hosting the largest collection of industry standards, specs, and regulations – the solution unlocks even greater value. Thread helps engineers quickly find relevant requirements buried in standards (see Figure 1), streamlining search and discovery within complex documents. The platform also manages and links critical information, supporting traceability and collaboration across teams and systems. This article explores the key benefits realized during recent customer trials and how this integration enhances efficiency, traceability, and compliance across the requirements lifecycle.
Additionally, this integration supports future advancements in engineering knowledge and digital transformation, ensuring organizations are prepared for ongoing developments in industry and internal standards and technology.
Challenge A: Referenced Standards Without Direct Specification – A Traceability Bottleneck
Traditionally, customers have stored internal standards, industry standards, and requirements documents (such as RFPs and customer specifications) in separate, disconnected systems. This fragmented environment limits the tracing of knowledge, slows verification, and introduces inefficiencies across the requirements engineering workflow.
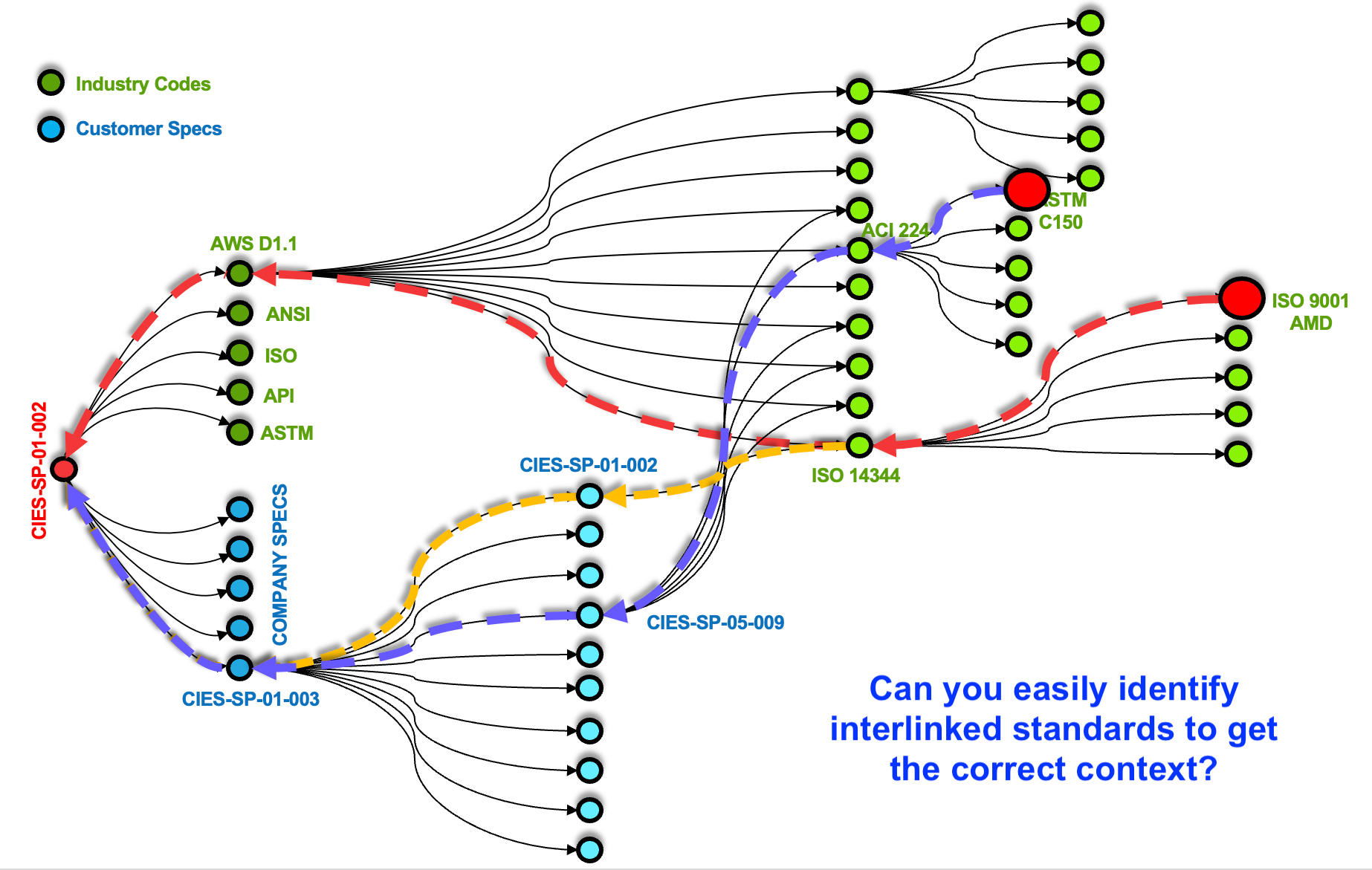
Consider a typical scenario: an engineer reviewing a new RFP encounters a requirement such as “Object X must meet the requirements of ISO YYY-X” or “Object X must be compliant with Standard YYY-X”. In such cases, the referenced standard is cited, but no specific clauses, criteria, or performance parameters are provided.
This forces the engineer to manually search for and open the referenced standard, interpret its content, and often trace through additional nested references—each introducing further complexity and time delays (see Figure 2). Engineers frequently need to filter through multiple references and documents to focus on the most relevant information. Without digital threads between the requirements and the standard, this process is inefficient and prone to error.
Tracking the date of industry or internal standard approvals or updates is also essential for compliance and visibility, ensuring that the correct and most current versions are referenced.
The Accuris Solution: Thread + Engineering Workbench Integration
When documents are ingested into Thread, the platform automatically detects referenced standards in text (Figure 3), and creates dynamic hyperlinks (aka Dynamic Links) to those documents within Engineering Workbench. With a single click, the engineer can open the standard in a new tab, eliminating the need to manually search the content library.

Beyond just access, the integration of Thread and EWB enables engineers to view and extract individual requirements directly from the referenced industry standard (Figure 4), streamlining the creation of requirements tables and accelerating the overall requirements development process by allowing users to create a set of requirements for easier management. This connected workflow significantly improves efficiency, accuracy, and tracing for engineering teams. The integration delivers positive results by enhancing collaboration, reducing errors, and improving the reliability of requirements extraction.
Engineers can further optimize their workflow by leveraging advanced features in Thread or Engineering Workbench, such as Watchlists and Micro-Alerts, which provide real-time notifications when specific clauses or sections within a standard are updated. Digital models are also integrated into the workflow, supporting enhanced traceability and decision-making throughout the engineering lifecycle. The platform functions as a comprehensive system for managing standards, requirements, and related workflows.
This proactive change monitoring simplifies requirements change management and ensures teams stay aligned with evolving standards. For organizations whose internal standards reference external industry specifications, these tools offer critical visibility into potential compliance risks and impact areas, empowering more informed and agile decision-making.
Additionally, engineers can create and embed section-level hyperlinks – generated using the Get Link feature – directly into a requirement’s metadata. These links open the standard document to the exact page and section, with the referenced requirement highlighted for immediate visibility. Users can also leave comments or receive notifications related to changes in industry or internal standards, further enhancing collaboration and engagement.
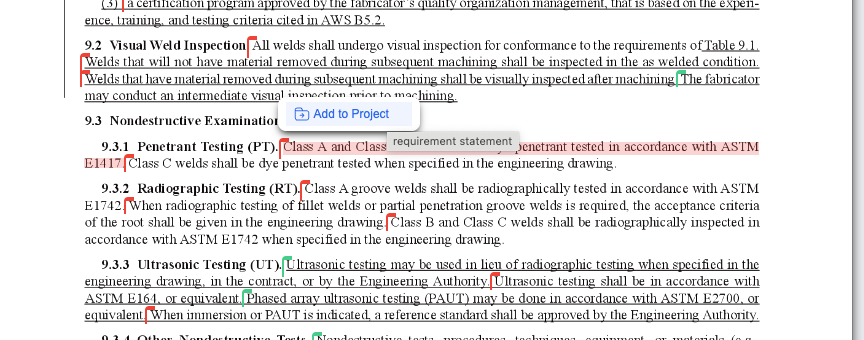
This capability is especially valuable for complex references, such as those involving tables or figures that are difficult to extract cleanly. For example, if a requirement states “shall comply with requirements from Table 9.1,” the engineer can insert a direct hyperlink to Section 9.1, ensuring precise and efficient access to the relevant information. (See Figure 5.)
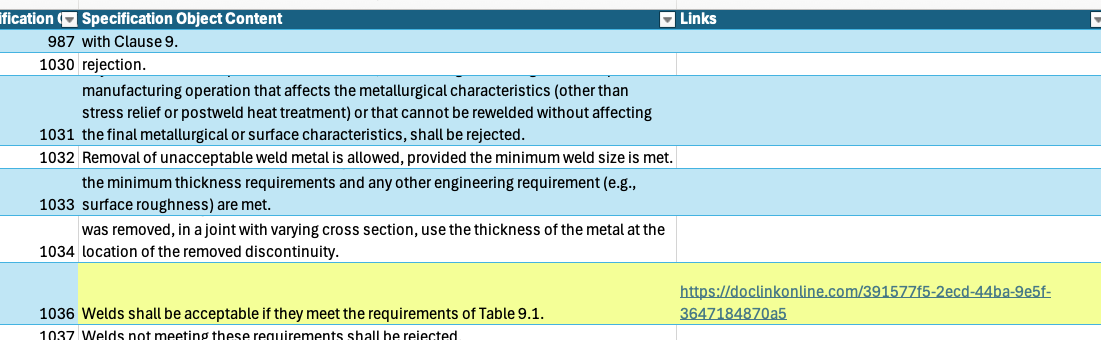
If other engineers need to refer to the elements of table 9.1, then they can simply click on the hyperlink to open that table in EWB (Figure 6)
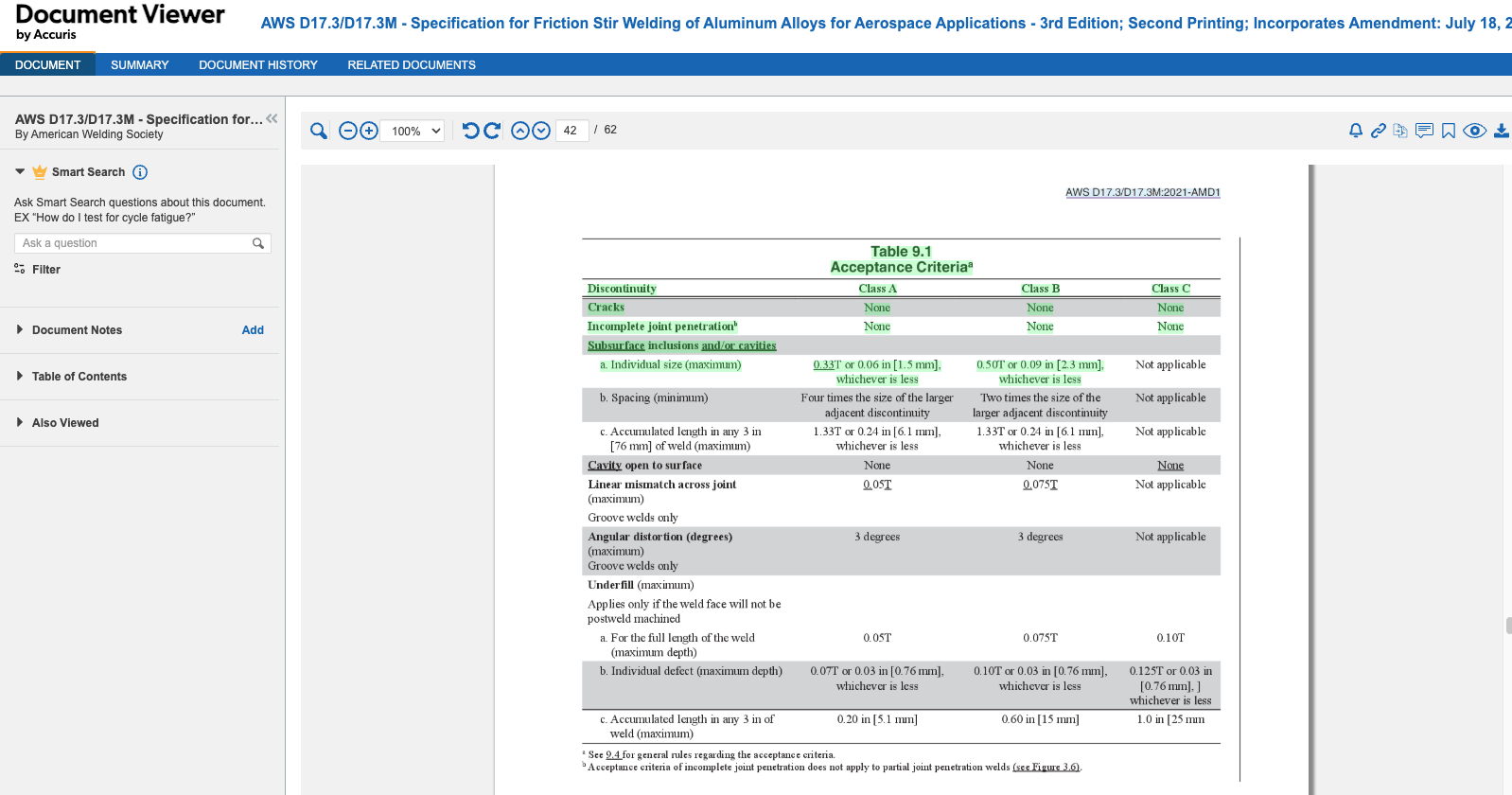
These two features, Micro-Alerts and Get Link, offer a new level of traceability to the source requirement and help manage changes.
Challenge B: Reducing the number of internal standards
Recently, several customers have indicated a strategic shift: reducing reliance on internal standards in favor of recognized industry standards. This transition is primarily driven by cost concerns and the risks associated with both over-engineering and under-engineering. Custom specifications, for example, often incur higher manufacturing costs, and in many cases, organizations cannot justify why their internal standards deviate from industry norms or even identify where those deviations exist.
Manually comparing a set of internal documents against multiple industry standards to identify overlaps, gaps, or redundancies is a resource-intensive task. To streamline this process, Thread’s Similar Analysis tool (Figure 7) enables engineers to quickly align internal standards with industry references, identify discrepancies, and support data-driven decisions, results, and precision. The tool’s semantic technology can identify all similar requirements from both other internal documents and industry standard content from Engineering Workbench. The tool also allows users to filter comparison results by different criteria, making it easier to focus on the most relevant changes. Additionally, users can compare different sets of standards or requirements to ensure comprehensive coverage and alignment.
Figure 7: Similar Analysis automatically finds similar requirements statements or clauses from other standards or internal documents, and allows side by side comparison.
Furthermore, the Similar Analysis tool helps identify duplicate or overlapping requirements across internal standards, enabling teams to consolidate redundant content and streamline internal documentation. It also helps detect and address potential problems in documentation, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring higher quality standards.
The effectiveness of the Similar Analysis tool in streamlining standardization and compliance processes helps organizations achieve greater precision, reliability, and results in their documentation and production workflows.
Conclusion: Unlock Efficiency with Integrations between Internal Standards, Industry Documentation, and Requirements
The integration of Thread with Engineering Workbench marks a transformative advancement in how engineering organizations manage, trace, and standardize their requirements. By automating the extraction of complex requirements documents and seamlessly linking them to authoritative industry standards, Thread not only saves valuable time but also significantly enhances precision, accuracy, traceability, and compliance across the engineering lifecycle.
This integration eliminates the inefficiencies of siloed content, manual cross-referencing, and prolonged searches for referenced industry or internal standards. Features like Dynamic Linking, real-time Micro-Alerts, and direct access to structured requirements empower engineers to focus on higher-value tasks, confident in the consistency and integrity of their results.
As organizations increasingly aim to reduce reliance on custom internal standards in favor of industry-aligned specifications, Thread offers a scalable and efficient solution that bridges requirements management with standards compliance. The result is a faster, smarter, and more connected engineering process designed to meet modern production and systems engineering demands.


